PostgreSQL Commands
สามารถใช้งานได้ดังนี้ 3 วิธีดังนี้
การใช้งานผ่านทาง sql shell (psql) connect database ด้วย psql
psql -U postgres postgres postgres=# CREATE DATABASE testdb1; postgres=# CREATE USER dbadmin1; postgres=# ALTER USER dbadmin1 WITH password 'password'; postgres=# GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE testdb1 to dbadmin1; postgres=# CREATE USER dbadmin2 WITH PASSWORD 'password'; postgres=# \du postgres=# \q (connect database ชื่อ testdb1 ด้วย user dbadmin1) [root@localhost ~]# psql -U dbadmin1 testdb1 Password for user dbadmin1: psql (10.2) Type "help" for help. testdb1=>การใช้งานผ่านคำสั่ง createdb command ผ่านทาง linux shell
การสร้าง user ผ่านคำสั่ง createuser และ การสร้างฐานข้อมูลผ่านคำสั่ง createdb
[root@localhost ~]# createuser --help
[root@localhost ~]# createuser -P -s -d dbadmin3 -U postgres
Enter password for new role:
Enter it again:
Password: (ใส่ password ของ postgres )
[root@localhost ~]# createdb --help
[root@localhost ~]# createdb --owner=dbadmin3 -U postgres testdb3
Password: (ใส่ password ของ postgres )
[root@localhost ~]# psql -U dbadmin3
Password for user dbadmin3:
psql: FATAL: database "dbadmin3" does not exist
(error เพราะ postgres จะพยายาม เปิด database ชื่อเดียวกับ user)
[root@localhost ~]## psql -U dbadmin3 -d testdb3
Password for user dbadmin3:
psql (10.2)
Type "help" for help.
testdb3=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
testdb1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
testdb3 | dbadmin3 | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
สรุปคำสั่งเบื้องต้น
testdb1=> \duแสดงรายชื่อ userpostgres=# \lแสดงฐานข้อมูลทั้งหมดpostgres=# \dtแสดงฐานข้อมูลทั้งหมดpostgres=# \cdatabase`` connect กับฐานข้อมูล
[root@localhost ~]# psql -U dbadmin1 testdb1
Password for user dbadmin1:
psql (10.2)
Type "help" for help.
testdb1=> \du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Member of
-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-----------
davide | | {}
dbadmin1 | | {}
dbadmin3 | Superuser, Create role, Create DB | {}
jonathan | | {}
postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {}
testdb1=> \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
testdb1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =Tc/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres+
| | | | | dbadmin1=CTc/postgres
testdb3 | dbadmin3 | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
(5 rows)
testdb1=> \c testdb3
You are now connected to database "testdb3" as user "dbadmin1".
testdb3=>
ตัวอย่าง 1 สร้างตาราง
- สร้างตาราง
employeesประกอบด้วย colume employee_id, first_name, last_name CREATE TABLE employees (employee_id int, first_name varchar, last_name varchar);- เพิ่ม record
INSERT INTO employees VALUES (1, 'John', 'Doe');
testdb3=> CREATE TABLE employees (employee_id int, first_name varchar, last_name varchar);
testdb3=> INSERT INTO employees VALUES (1, 'John', 'Doe');
testdb3=> \d employees
Table "public.employees"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
-------------+-------------------+-----------+----------+---------
employee_id | integer | | |
first_name | character varying | | |
last_name | character varying | | |
testdb3=> SELECT * FROM employees;
testdb3=> \dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+-----------+-------+----------
public | employees | table | dbadmin1
(1 row)
Information_schema meta data
ใช้คำสั่ง SELECT ค้นหาชื่อ colume name จากตาราง information_schema meta-data
SELECT
COLUMN_NAME
FROM
information_schema.COLUMNS
WHERE
TABLE_NAME = 'employees';
แสดง tables ใช้ pg_catalog schema
SELECT
*
FROM
pg_catalog.pg_tables
WHERE
schemaname != 'pg_catalog'
AND schemaname != 'information_schema';
ตัวอย่าง 2 สายการบิน
ตัวอย่าง ด้านล่าง แสดงเส้นทางการเดินระหว่างเมืองพร้อมระยะทาง
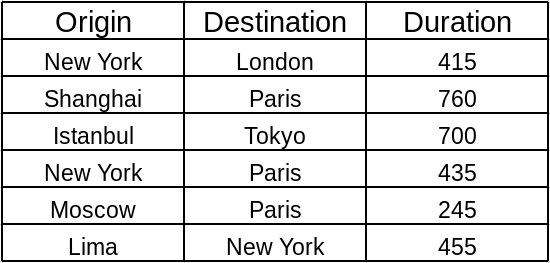
Postgresql data type
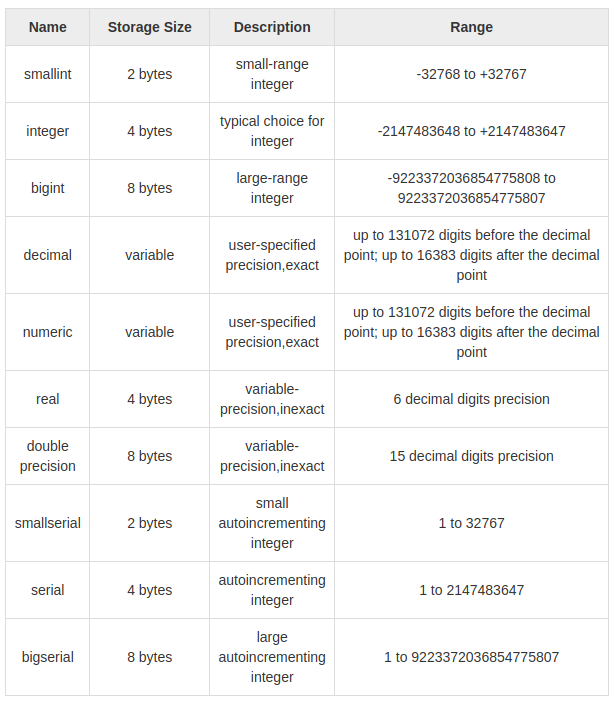
CREATE TABLE
- สร้างไฟล์ ชื่อ
flight-createtable.sqlมีเนื้อหาดังต่อไปนี้
.. literalinclude:: _static/code/flight-createtable.sql
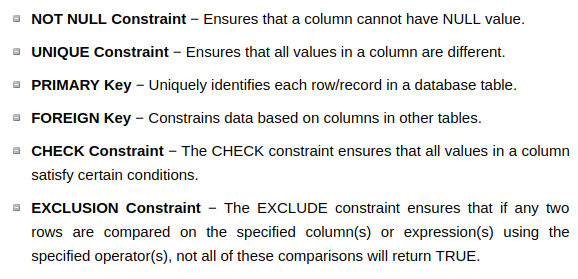
มีการกำหนด constraint NOT NULL ในไฟล์ เพื่อป้องกันค่าว่าง (ไม่กำหนดค่า)
เป็น sql syntax เมื่อ import เข้าสู่ฐานข้อมูล ก็ถูกแปลความ สามารถที่จะนำเข้าสู่ database
ได้ 2 แบบ ได้แก่การใช้การ < หรือจะ copy โดยตรงไปยัง postgres shell ก็ได้
[root@localhost ~]# psql -U dbadmin3 testdb3 < flight-createdb.sql
Password for user dbadmin3:
CREATE TABLE
สามารถใช้ option ``-c`` เพื่อส่งคำส่งไปยัง postgres shell
[root@localhost ~]# psql -U dbadmin3 testdb3 -c "\d"
Password for user dbadmin3:
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+----------------+----------+----------
public | employees | table | dbadmin1
public | flights | table | dbadmin3
public | flights_id_seq | sequence | dbadmin3
INSERT TABLE
รูปแบบ sql syntax::
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME (column1, column2, column3,...columnN)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...valueN);
.. literalinclude:: _static/code/flight-insert.sql
[root@localhost ~]# psql -U dbadmin3 testdb3 -c "select * from flights"
Password for user dbadmin3:
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
1 | New York | London | 415
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
4 | New York | Paris | 435
5 | Moscow | Paris | 245
6 | Lima | New York | 455
(6 rows)
SELECT and WHERE
รูปแบบ sql syntax::
SELECT column1, column2, columnN
FROM table_name
WHERE [CONDITION | EXPRESSION];
การใช้งานจะใช้งานร่วมกัน ระหว่าง Comparison และ Logical
PostgreSQL Comparison Operators
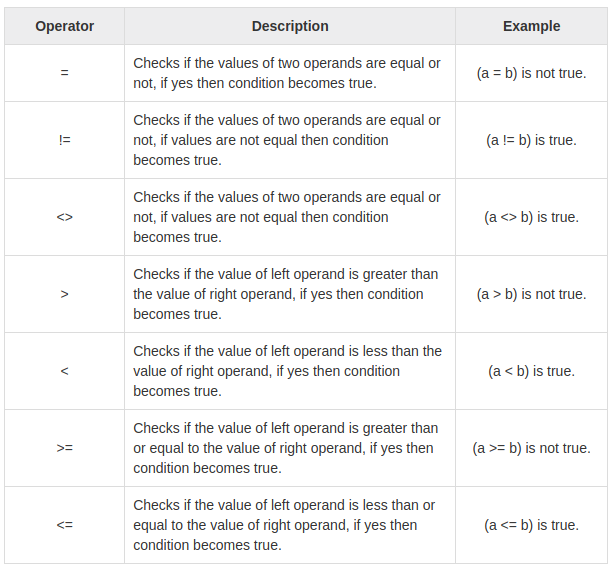
PostgreSQL Logical Operators

SELECT * FROM flights WHERE duration > 500;
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
(2 rows)
SELECT * FROM flights WHERE destination = 'Paris'
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
4 | New York | Paris | 435
5 | Moscow | Paris | 245
(3 rows)
SELECT * FROM flights WHERE destination = 'Paris' AND duration > 500;
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
(1 row)
Aggregate Functions
Aggregate function คือการคำนวนแล้วได้ผลลัพท์ เพียงอย่างเดียว จากการคำนวนของชุดข้อมูล ชุดใดๆ
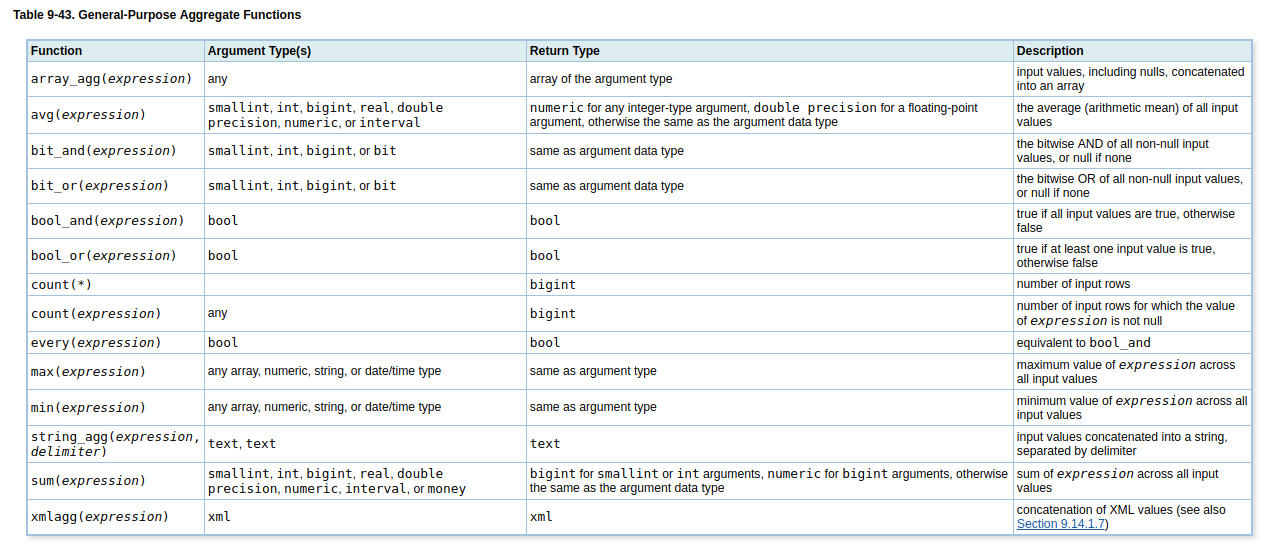
- ต้องการหาค่าเฉลี่ย
avg
SELECT AVG(duration) FROM flights;
avg
----------------------
501.6666666666666667
(1 row)
SELECT AVG(duration) FROM flights WHERE origin='New York';
avg
----------------------
425.0000000000000000
(1 row)
- ต้องการนับจำนวน record
count
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM flights;
count
-------
6
(1 row)
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM flights WHERE origin = 'New York';
count
-------
2
(1 row)
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM flights WHERE origin = 'Moscow';
count
-------
1
(1 row)
- ต้องการหาค่า ต่ำสุด และ สูงสุด
testdb3=# SELECT MIN(duration) FROM flights;
min
-----
245
(1 row)
testdb3=# SELECT MAX(duration) FROM flights;
max
-----
760
(1 row)
- เงื่อนไข IN, NOT IN CONDITION
postgres สามารถค้นหา ด้วย IN condition
รูปแบบ sql syntax
expression IN (value1, value2, .... value_n);
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights WHERE origin IN ('New York', 'Lima');
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
1 | New York | London | 415
4 | New York | Paris | 435
6 | Lima | New York | 455
(3 rows)
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights WHERE origin NOT IN ('New York', 'Lima');
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
5 | Moscow | Paris | 245
(3 rows)
- ค้นหา LIKE, NOT LIKE
รูปแบบ sql syntax
string LIKE pattern
string NOT LIKE pattern
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights WHERE origin LIKE '%a%';
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
6 | Lima | New York | 455
(3 rows)
.. warning::
Like ใช้ได้กับ text หากต้องการ ค้นหา Attributes ที่เป็น integer ต้องทำการ cast
เป็น text ด้วย ``::TEXT``
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights WHERE duration LIKE '%7%';
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights WHERE duration::TEXT LIKE '%7%';
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
(2 rows)
- ปรับปรุง UPDATE
รูปแบบ sql syntax
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2...., columnN = valueN
WHERE [condition];
ใช้สำหรับการปรับปรุงค่าของ Attributes
UPDATE flights
SET duration = 430
WHERE origin = 'New York'
AND destination = 'London';
run
testdb3=# UPDATE flights
testdb3-# SET duration = 430
testdb3-# WHERE origin = 'New York'
testdb3-# AND destination = 'London';
UPDATE 1
- ลบ DELETE
รูปแบบ sql syntax
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE [condition];
run
DELETE FROM flights WHERE origin = 'New York';
- จำกัดจำนวน LIMIT
จำกัด จำนวนผลลัพท์ ที่ได้จาก query
run
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights LIMIT 2;
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
(2 rows)
- จัดลำดับ ORDER
เรียงลำดับผลลัพท์ โดย เลือก attribute เรียงจากน้อยไปหามาก ASC หรือเรียงจากมากไปหาน้อย DSC
run
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights ORDER BY duration ASC;
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
5 | Moscow | Paris | 245
1 | New York | London | 430
4 | New York | Paris | 435
6 | Lima | New York | 455
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
(6 rows)
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights ORDER BY duration ASC LIMIT 3;
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
5 | Moscow | Paris | 245
1 | New York | London | 430
4 | New York | Paris | 435
(3 rows)
testdb3=# SELECT * FROM flights ORDER BY duration DESC;
id | origin | destination | duration
----+----------+-------------+----------
2 | Shanghai | Paris | 760
3 | Istanbul | Tokyo | 700
6 | Lima | New York | 455
4 | New York | Paris | 435
1 | New York | London | 430
5 | Moscow | Paris | 245
(6 rows)
- จัดกลุ่ม GROUP BY
โดยส่วนมากใช้งานร่วมกับ aggregate fuction SUM, COUNT , HAVE
รูปแบบ sql syntax
SELECT column-list
FROM table_name
WHERE [ conditions ]
GROUP BY column1, column2....columnN
ORDER BY column1, column2....columnN
run
testdb3=# SELECT origin FROM flights GROUP BY origin;
origin
----------
Shanghai
Moscow
Istanbul
New York
Lima
(5 rows)
testdb3=# SELECT origin,COUNT(*) FROM flights GROUP BY origin;
origin | count
----------+-------
Shanghai | 1
Moscow | 1
Istanbul | 1
New York | 2
Lima | 1
(5 rows)
testdb3=# SELECT origin,COUNT(*) FROM flights GROUP BY origin
testdb3-# HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
origin | count
----------+-------
New York | 2
(1 row)
- คีย์ Foreign Keys พิจารณาตารางที่ได้เพิ่มเติม โค้ดสนามบิน
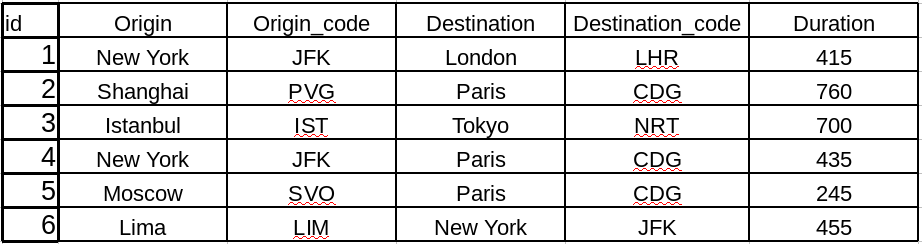
เมื่อเราแยก ตารางออกมาได้ 2 ตารางดังนี้
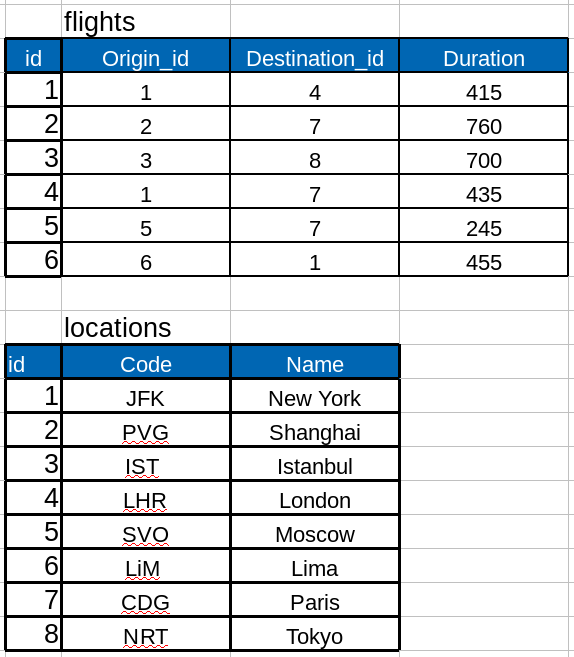
และเพิ่มเติมตารางผู้โดยสารที่โดยสายการบิน
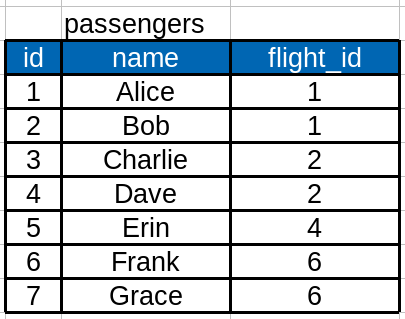
- สร้างตาราง location, flight, passengers ดังนี้
- vim flight-passengers.sql
DROP TABLE flights;
CREATE TABLE locations (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
code VARCHAR NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE flights (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
origin_id INTEGER REFERENCES locations,
destination_id INTEGER REFERENCES locations,
duration INTEGER NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE passengers (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
flight_id INTEGER REFERENCES flights
);
References จะใช้เชื่อมโยงกันระหว่าง Foreign key ไปยัง PRIMARY อีกตารางหนึ่ง
- Insert ข้อมูลในฐานข้อมูล database
- สร้าง ไฟล์
vim flight-data.sqlด้วยข้อมูลด้านล่างนี้
- สร้าง ไฟล์
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('JFK','New York');
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('PVG','Shanghai');
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('IST','Istanbul');
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('LHR','London');
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('SVO','Moscow');
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('Lim','Lima');
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('CDG','Paris');
INSERT INTO locations
(code,name)
VALUES ('NRT','Tokyo');
INSERT INTO flights
(origin_id, destination_id, duration)
VALUES (1, 4, 415);
INSERT INTO flights
(origin_id, destination_id, duration)
VALUES (2, 7, 415);
INSERT INTO flights
(origin_id, destination_id, duration)
VALUES (3, 8, 415);
INSERT INTO flights
(origin_id, destination_id, duration)
VALUES (1, 7, 415);
INSERT INTO flights
(origin_id, destination_id, duration)
VALUES (5, 7, 415);
INSERT INTO flights
(origin_id, destination_id, duration)
VALUES ('6', '1', 415);
INSERT INTO passengers
(name, flight_id)
VALUES ('Alice',1);
INSERT INTO passengers
(name, flight_id)
VALUES ('Bob',1);
INSERT INTO passengers
(name, flight_id)
VALUES ('Charlie',2);
INSERT INTO passengers
(name, flight_id)
VALUES ('Dave',2);
INSERT INTO passengers
(name, flight_id)
VALUES ('Erin',4);
INSERT INTO passengers
(name, flight_id)
VALUES ('Frank',6);
INSERT INTO passengers
(name, flight_id)
VALUES ('Grace',6);
Alice อยู่ เครื่องบินลำไหน
SELECT * FROM passengers WHERE name='Alice';
id | name | flight_id
----+-------+-----------
1 | Alice | 1
(1 row)
SELECT * FROM flights WHERE id=1;
id | origin_id | destination_id | duration
----+-----------+----------------+----------
1 | 1 | 4 | 415
(1 row)
SELECT * FROM locations WHERE id=1;
id | code | name
----+------+----------
1 | JFK | New York
(1 row)
SELECT * FROM locations WHERE id=4;
id | code | name
----+------+--------
4 | LHR | London
(1 row)
Basic SQL Join type
Join เป็นการค้นหาจากตารางที่มากกว่า 1 ตาราง ให้เป็นการค้นหาครั้งเดียว
Syntax
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
สองตารางที่มีความสัมพันธ์กัน โดยที่ทั้งสองตารางจะมี attribute (colume) ตรงกัน
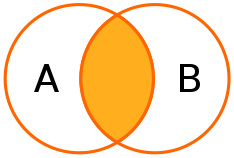
testdb3=# SELECT origin_id,destination_id,name FROM flights
testdb3-# JOIN passengers
testdb3-# ON flights.id=passengers.flight_id;
origin_id | destination_id | name
-----------+----------------+---------
1 | 4 | Alice
1 | 4 | Bob
2 | 7 | Charlie
2 | 7 | Dave
1 | 7 | Erin
6 | 1 | Frank
6 | 1 | Grace
(7 rows)
เพิ่มเงื่อนไข where
testdb3=# SELECT origin_id,destination_id,name FROM flights
testdb3-# JOIN passengers
testdb3-# ON flights.id=passengers.flight_id
testdb3-# WHERE name='Alice';
origin_id | destination_id | name
-----------+----------------+-------
1 | 4 | Alice
(1 row)
ใน sql เมื่อมีการระบุ join จะหมายถึง inner join ที่ตรงตามเงื่อนไข เท่านัน แต่หากเป็น LEFT JOIN ผลที่ได้ก็จะพยายามรักษา จำนวนสมาชิกใน ตารางทางซ้ายไว้ ให้ครบถ้วน ทำให้มีบางส่วนของผลที่จะได้เป็นค่าว่าง เนื่องจาก ไม่ match
LEFT JOIN
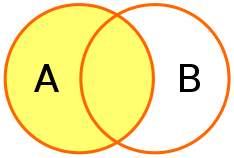
testdb3=# SELECT origin_id,destination_id,name FROM flights
testdb3-# LEFT JOIN passengers
testdb3-# ON flights.id=passengers.flight_id;
origin_id | destination_id | name
-----------+----------------+---------
1 | 4 | Alice
1 | 4 | Bob
2 | 7 | Charlie
2 | 7 | Dave
1 | 7 | Erin
6 | 1 | Frank
6 | 1 | Grace
5 | 7 |
3 | 8 |
(9 rows)
RIGHT JOIN
รูปแบบ
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
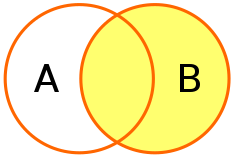
testdb3=# SELECT origin_id,destination_id,name FROM flights
testdb3-# RIGHT JOIN passengers
testdb3-# ON flights.id=passengers.flight_id;
origin_id | destination_id | name
-----------+----------------+---------
1 | 4 | Alice
1 | 4 | Bob
2 | 7 | Charlie
2 | 7 | Dave
1 | 7 | Erin
6 | 1 | Frank
6 | 1 | Grace
(7 rows)
การใช้งาน index เป็นการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของการค้นหา โดยการเลือก attribute ที่ต้องการจากตาราง Syntax
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (column1, column2, ...);
DROP INDEX index_name;
ทดสอบ
testdb3=# CREATE INDEX flight_index ON flights (origin_id, destination_id)
testdb3=# SELECT * from pg_indexes WHERE tablename = 'flights';
ทดสอบ
testdb3=# \d flights
Table "public.flights"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
----------------+---------+-----------+----------+-------------------------------------
id | integer | | not null | nextval('flights_id_seq'::regclass)
origin_id | integer | | |
destination_id | integer | | |
duration | integer | | not null |
Indexes:
"flights_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
"flight_index" btree (origin_id, destination_id) <----- index
Foreign-key constraints:
"flights_destination_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (destination_id) REFERENCES locations(id)
"flights_origin_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (origin_id) REFERENCES locations(id)
Referenced by:
TABLE "passengers" CONSTRAINT "passengers_flight_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (flight_id) REFERENCES flights(id)
NESTED query
SQL สามารถนำ query มารัน ซ้อนกันได้ ดังนี้
SELECT * FROM flights WHERE id IN (SELECT flight_id FROM passengers GROUP BY
flight_id HAVING COUNT(*) > 1 );
id | origin_id | destination_id | duration
----+-----------+----------------+----------
6 | 6 | 1 | 415
2 | 2 | 7 | 415
1 | 1 | 4 | 415
(3 rows)
Workshop customer-orders
ให้สร้างตารางเพื่อเก็บข้อมูล ความสัมพันระหว่าง customer และ order ดังต่อไปนี้
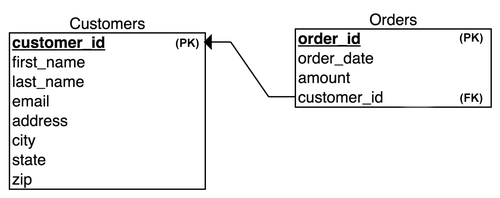
ตัวอย่างข้อมูล
และ
หลังจาก insert แล้ว ลองทดสอบคำสั่ง SQL ดังนี้
คำสั่ง1
select order_date, order_amount
from customers
join orders
on customers.customer_id = orders.customer_id
where customer_id = 3;
คำสั่ง2
select first_name, last_name, order_date, order_amount
from customers c
left join orders o
on c.customer_id = o.customer_id;
คำสั่ง3
select first_name, last_name, order_date, order_amount
from customers c
left join orders o
on c.customer_id = o.customer_id
where order_date is NULL;
คำสั่ง4
select first_name, last_name, order_date, order_amount
from customers c
right join orders o
on c.customer_id = o.customer_id;
คำสั่ง5
select first_name, last_name, order_date, order_amount
from customers c
right join orders o
on c.customer_id = o.customer_id
where first_name is NULL;
คำสั่ง6
select first_name, last_name, order_date, order_amount
from customers c
full join orders o
on c.customer_id = o.customer_id;
script sql
DROP TABLE customers;
DROP TABLE orders;
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR NOT NULL,
address VARCHAR NOT NULL,
city VARCHAR NOT NULL,
state VARCHAR NOT NULL,
zipcode INTEGER
);
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
order_date DATE NOT NULL,
AMOUNT NUMERIC(18,2) NOT NULL,
customer_id INTEGER REFERENCES customers
);
INSERT INTO customers
(first_name,last_name,email,address,city,state,zipcode)
VALUES
('George','Washington','[email protected]','3200 Mt Vernon Hwy','Mount Vernon','VA',22121),
('John','Adams','[email protected]','1250 Hancock St','Quincy','MA',02169),
('Thomas','Jefferson','[email protected]','931 Thomas Jefferson Pkwy','Charlottesville','VA',22902),
('James','Madison','[email protected]', '11350 Constitution Hwy Orange', 'Orange', 'VA', 22960 ),
('James', 'Monroe', '[email protected]', '2050 James Monroe Parkway', 'Charlottesville', 'VA', 22902 );
INSERT INTO orders
(order_date,AMOUNT,customer_id)
VALUES
('07/04/1776','234.56',1),
('03/14/1760','78.50',3),
('05/23/1784','124.00',2),
('09/03/1790','65.50',4),
('07/21/1795','25.50',1),
('11/27/1787','14.40',5);